Your Content Goes Here
With the continuous upgrading and transformation of modern technology and use requirements, today’s technology has upgraded and transformed the cable fault tester into a power cable fault comprehensive tester, which is more convenient for finding cable fault points and detection distances. It is no longer difficult for the cable fault tester to locate the cable fault point accurately. So what is the method of the cable fault tester to find the cable fault point?
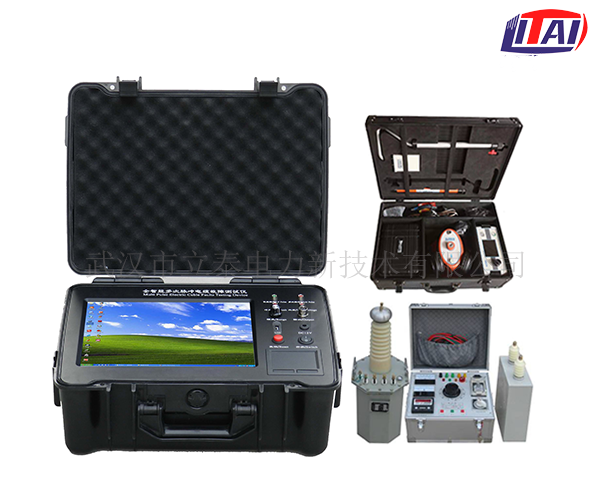
The cable fault tester can test the cable’s high-resistance flashover fault, high and low-resistance grounding, short circuit and cable disconnection, poor contact and other faults. Due to the variability of the environment in which power cables are laid, coupled with the application of new materials for cables and their accessories in the cable line, it is increasingly difficult to locate faults on the power cable site.
Which method should be used to find the location of the cable fault point? The difficulty of field cable fault location is highlighted in the fault location of directly buried power cable lines. At present, for high-resistance faults in power cable lines, although there are related classic technical documents and advanced fault detectors available. But when using a professional cable fault locator to locate in the field, sometimes we will encounter some special difficult faults that cannot be located. For example, partial creepage flashover faults on the insulating surface of medium voltage cross-linked power cable terminals and intermediate heads, accurate positioning of metallic short-circuit faults, etc., using professional cable fault locators often appears powerless or incompetent.
The principle of the cable fault tester is that the host uses the principle of time domain reflection (TDR) to transmit a series of electric pulses to the cable under test, and receive the reflected pulses caused by the impedance change in the cable, and then according to the propagation speed of the electric wave in the cable and The time represented by the characteristic inflection point of the two reflected waves, the distance from the fault point to the test end can be measured: S=VT/2
In the formula: S represents the distance from the fault point to the test end
V represents the propagation speed of electric waves in the cable
T represents the time required for the electric wave to propagate back and forth in the cable
In this way, when V is known and T has been measured, the distance S from the fault point to the test terminal can be calculated.
Cable fault tester finds the method of cable fault point. There are two methods for cable fault test: low voltage pulse method and flash current method. The principle of the cable fault tester can be used to find the cable fault point. How to find the cable fault point of the cable fault tester must choose a suitable test method, you can use the cable tester host to conduct a rough test of the cable fault; but different methods should be used for different cable faults, such as low resistance faults (open circuit, short circuit, etc.) Use the low-voltage pulse method to test; while high-resistance faults (leakage, flashover, etc.) are tested by the high-voltage flashover method; only choose the appropriate test method, and use the tester host to conduct a rough measurement of the distance to the cable.